Database and Migrations
You can config Database in the .env file. By default, Laravel has MySQL configuration.
For example, I configured my details
DB_CONNECTION=mysql
DB_HOST=127.0.0.1
DB_PORT=3306
DB_DATABASE=Laravel_tutorials
DB_USERNAME=root
DB_PASSWORD=
So how it connects the database, In your root folder config/database.php file will read the .env file configuration.
Migrations:
Migrations are most likely a version control for your database.
Advantages
- You can easily allow your team to modify database schema and share to everyone in the application
- No headache to add a new column in the database manually. This migration will help all teammates into one path.
Now check with artisan command
php artisan migrate |
| php artisan migrate |
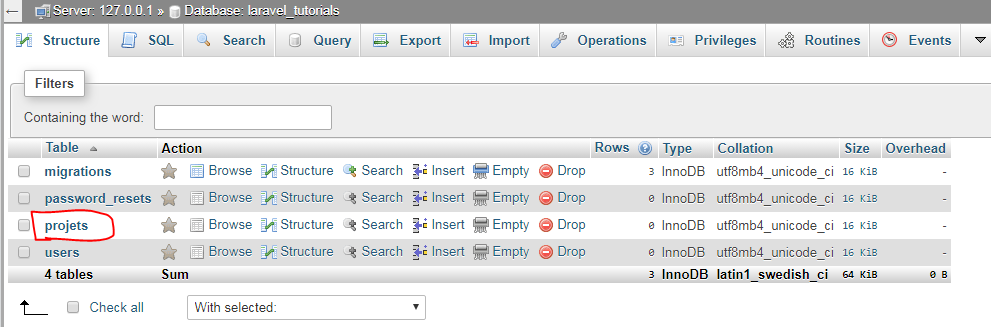
This command will create basic users,password_resets and migrations tables.
You can undo previous migration using rollback command
php artisan migrate:rollback |
| PHP Artisan Migrate rollback |
 |
| PHP Artisan Migrate rollback database |
All these migrations will store at database/migrations.
Modify Column name:
Suppose If I want to rename the Column name. To do this go to the migrations files at database/migrations.
Now I'll modify the user's table column name filed "name" to "username"
$table->string('name'); to $table->string('username');
Now you have two options to modify this in the database.
Option 1
php artisan migrate:rollback
php artisan migrate
Option 2
php artisan migrate: fresh
Note: This command drops all the tables. So never run this command when your project on Production
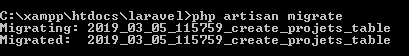
Let's make the new migrate file.
php artisan make:migration create_projets_table |
| php artisan make:migration create_projets_table |
Note: All php artisan make: * commands generate new files and classes.
Hint: Whenever you stuck with command. You can take "help" from help tag. Ex: php artisan help make: migration
After running this command, Check the root folder at database/migrations. The new file will be created.
Inside the file, By default Larvel creates up() and Down() methods.
What is up() and down() methods? How it works?
up() method allows running migrate function. Which means when you run migrate. It will run the up() method.
Similarly. Down() method works as undoing the up() method. We can say that migrate: rollback. So up() create the table and down() drops the table.
By default, Schema builds like below.
public function up()
{
Schema::create('projets', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->bigIncrements('id');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
Now add few more column fields (title,description) in this projects table.
public function up()
{
Schema::create('projets', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->bigIncrements('id');
$table->string('title');
$table->text('description');
$table->timestamps();
});
} |
| php artisan migrate |
As well as undoing
if you comment down() method inside the code. Rollback will not work. because it is not defined to down() method to rollback.
public function down()
{
//Schema::dropIfExists('projets');
}
To check migration files status that those files are running or not with below commands
php artisan migrate:status
To check if there is any pending migrate files to run
php artisan migrate --pretend
In Laravel, you can't directly run a single migration file using php artisan migrate like you can with seeders. However, there are a few ways to handle running a specific migration:
php artisan migrate --path=/database/migrations/2024_01_01_123456_create_users_table.php
###



Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you :)